Having trouble with a printer that won’t print, a webcam that won’t connect, or audio that suddenly stops working?
These frustrating issues often stem from missing or outdated drivers in Windows 11.
As someone who’s helped numerous users resolve driver-related problems, I’ll walk you through three methods to find and install the right drivers – from using Windows’ built-in tools to advanced manual techniques.
Method 1: Installing Drivers Through Windows Update
Windows Update is often the safest and most reliable way to get your missing drivers. Drivers can be installed through two methods in Windows Update:
Regular Windows Updates: Important driver updates are often included in regular Windows Updates. To check:
- Press the Windows key and click the Settings icon
- Select Windows Update from the left navigation pane
- Click “Check for updates”
- Install any available updates
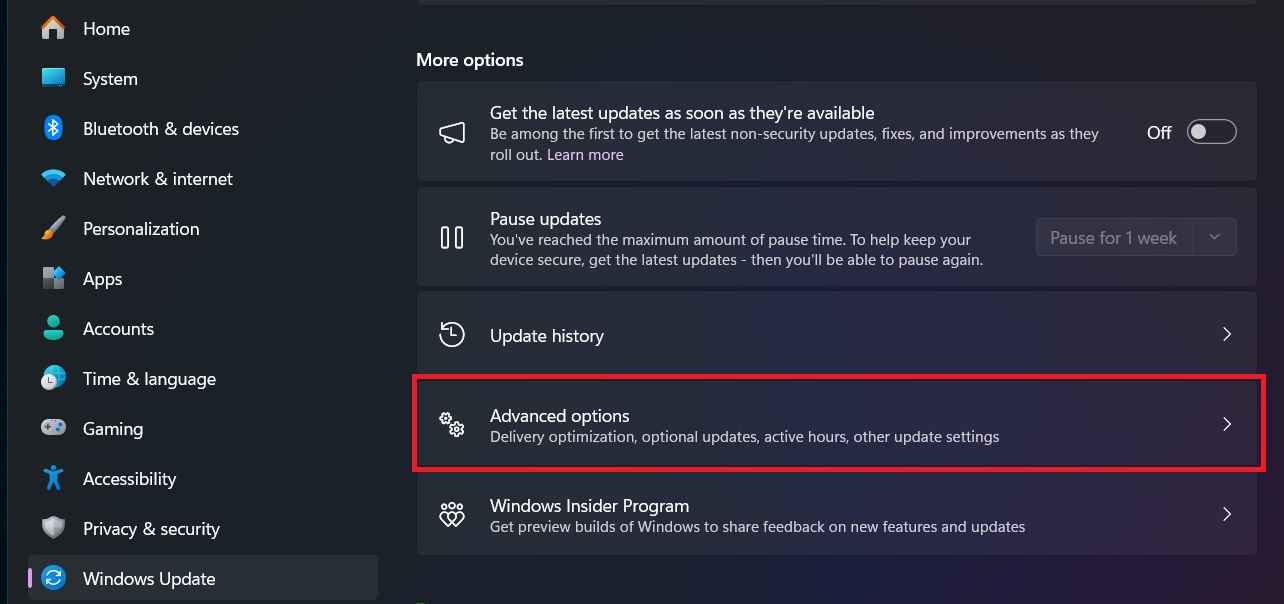
Optional Updates: Additional driver updates may be available in the Optional Updates section:
- In Windows Update, click “Advanced options”

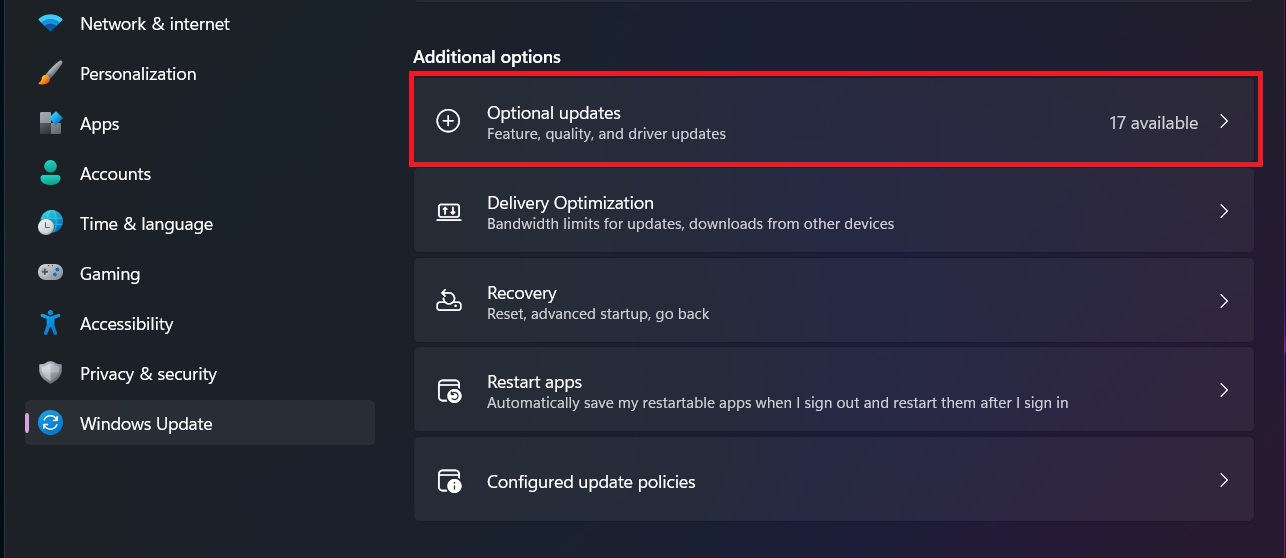
- Under “Additional options,” select “Optional updates”

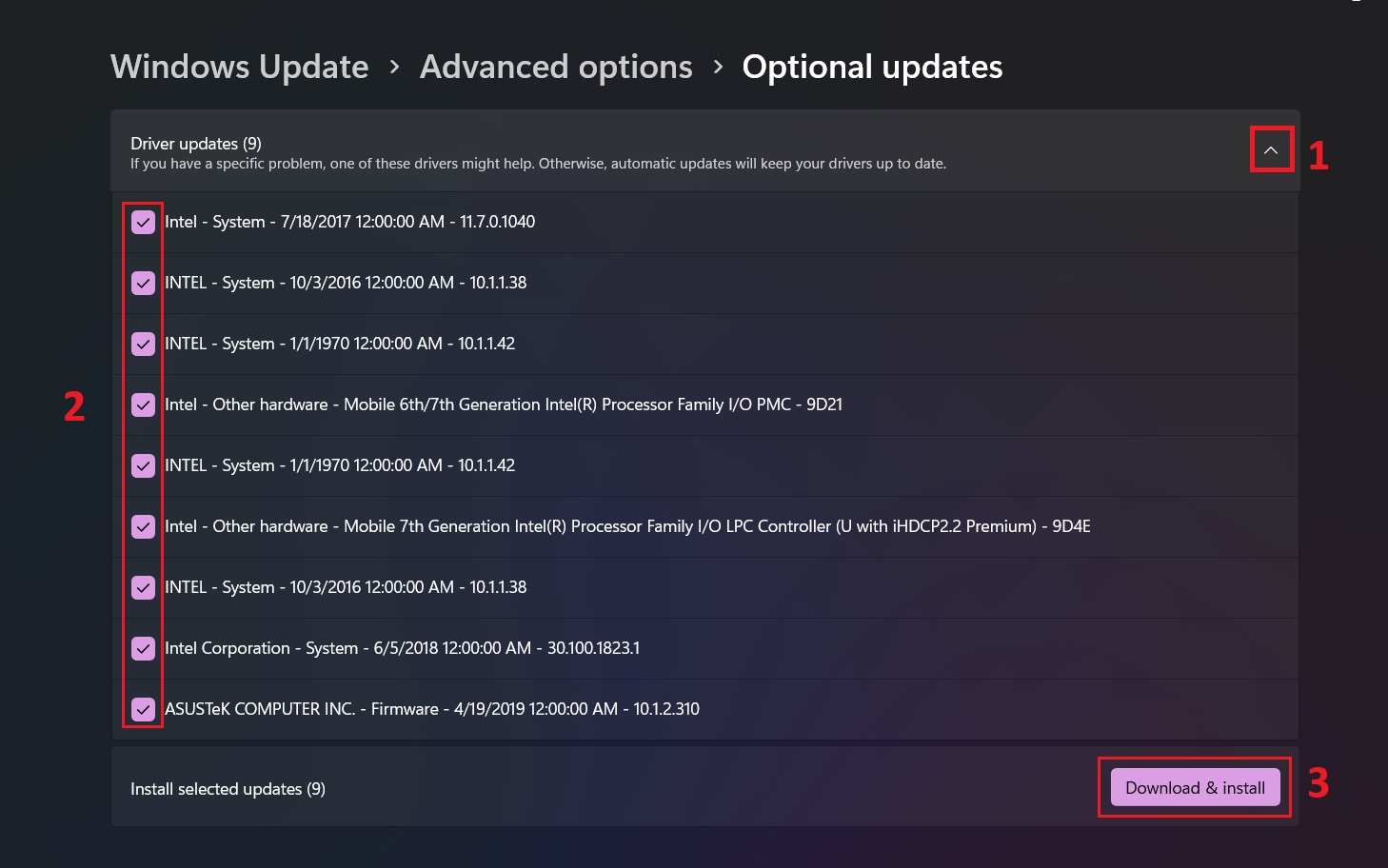
- Look for the “Driver updates” section
- Check the boxes next to any available driver updates
- Click the blue “Download and install” button

- Restart your computer to complete the installation
Pro Tip: Even if you don’t see any driver updates listed, it’s worth checking both sections periodically as Microsoft regularly adds new drivers to Windows Update.
Method 2: Using Device Manager
Device Manager is a built-in Windows tool that can help identify and fix driver issues. To begin, right-click the Windows button and select “Device Manager” from the menu.
Once opened, you’ll need to expand all categories in the device list to get a complete view of your system’s hardware.
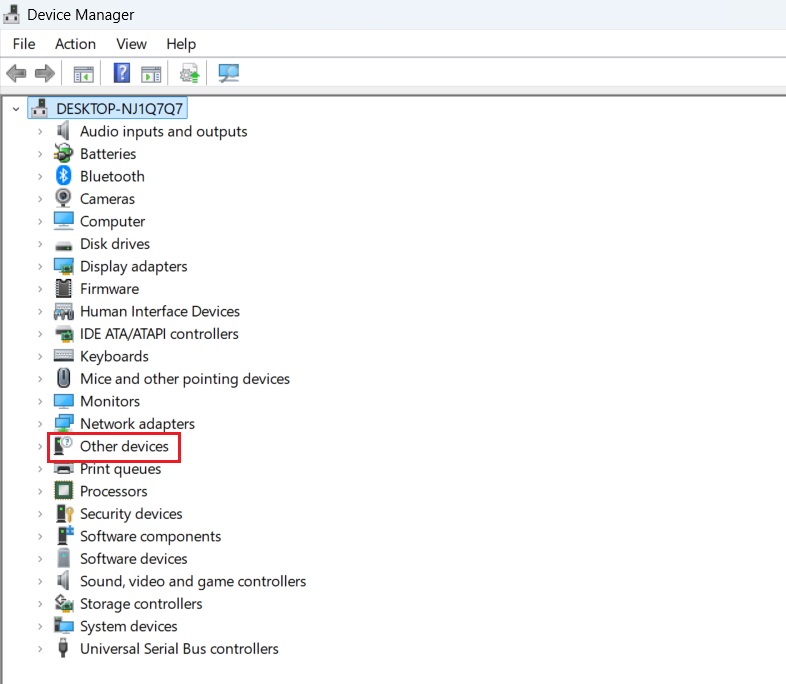
When examining the device list, pay special attention to any devices marked with a yellow exclamation mark (!), as this indicates a driver problem. To address the issue, right-click the problematic device and select “Update driver” from the context menu.
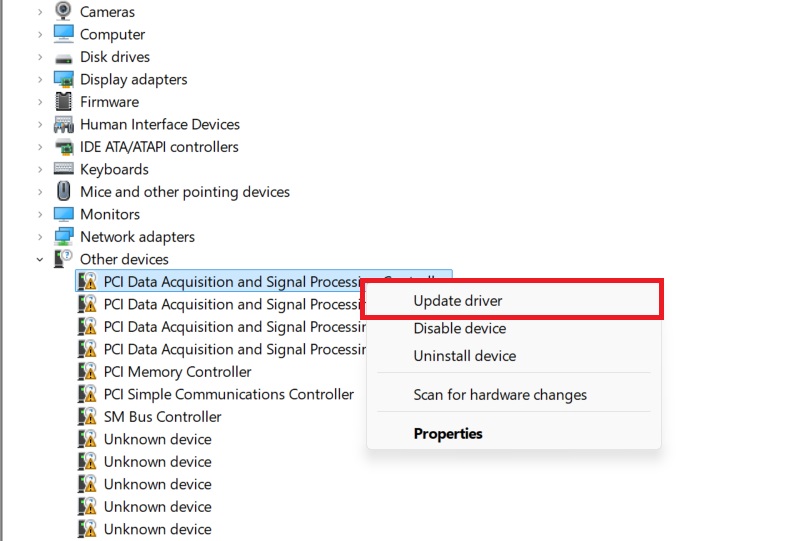
Windows will present you with two options: you can either search automatically for drivers, which allows Windows to search online for the latest driver, or browse your computer for drivers if you’ve already downloaded them manually.
After selecting your preferred method, simply follow the on screen prompts to complete the installation process. Your computer may need to restart to apply the changes, so save any open work before proceeding with the restart when prompted.
Troubleshooting Tip: If Windows can’t find a driver automatically, note down the hardware ID (right-click device → Properties → Details → Hardware Ids) and search for it on the manufacturer’s website.
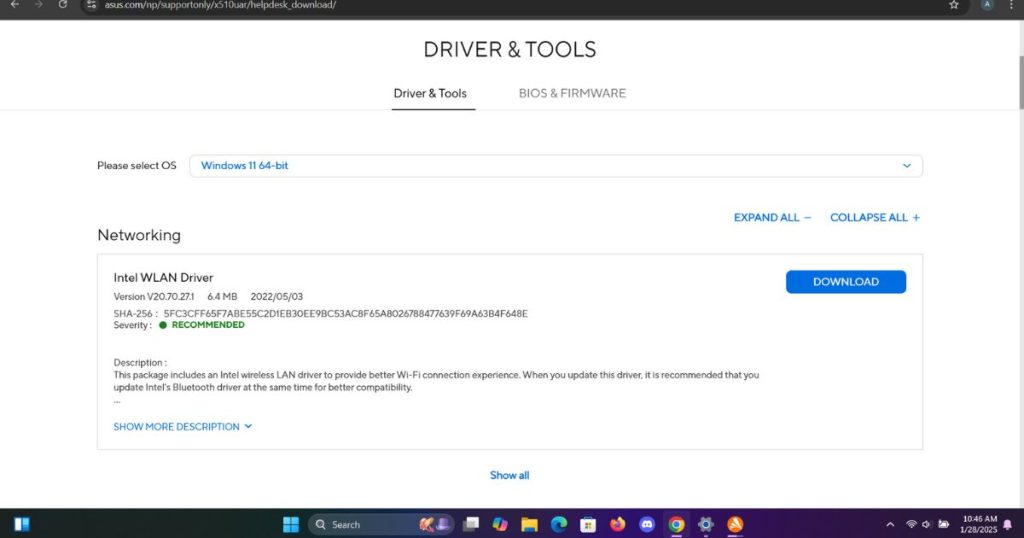
Method 3: Through the manufacturer’s website
IMPORTANT SECURITY NOTE: Always ensure you’re downloading from the official manufacturer’s website. Many fake websites distribute malware disguised as driver updates. Double-check the URL before downloading any drivers.
- First, identify your computer or device model:
- For prebuilt PCs: Look for a service tag or serial number (usually on a sticker on your computer)
- For custom PCs: You’ll need to know the model numbers of individual components (motherboard, GPU, etc.)
- Visit the appropriate support website:
- Dell: dell.com/support
- HP: support.hp.com
- Lenovo: support.lenovo.com
- ASUS: asus.com/support
- MSI: msi.com/support
- For individual components:
- Graphics: nvidia.com/download or amd.com/support
- Intel: intel.com/support
- On the manufacturer’s site:
- Enter your service tag/serial number or navigate through the product categories to find your model

- Some sites have automatic detection tools that scan your system
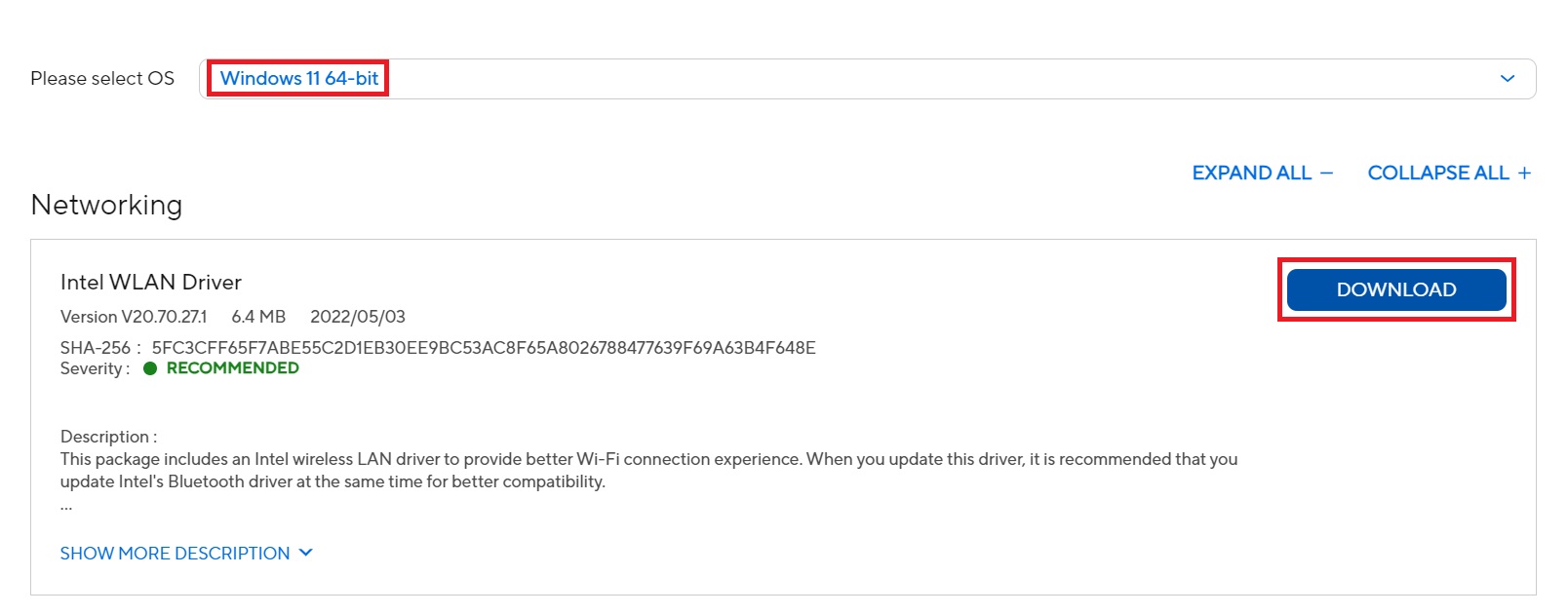
- Find the Drivers & Downloads section:
- Look for “Windows 11” specific drivers
- Pay attention to your system type (32-bit vs 64-bit)
- Drivers are usually sorted by category (Display, Network, Audio, etc.)
- Check the release date to get the latest version

- Download the drivers:
- Most come as .exe files (self-installing)
- Some come as .zip files (need to be extracted)
- Save them in a location you can easily find
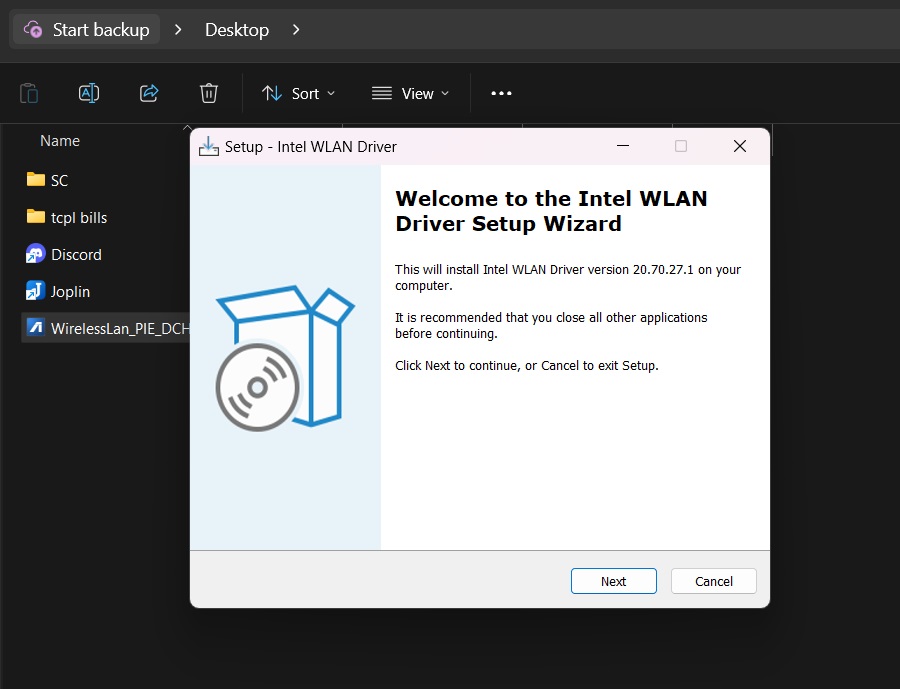
- Install the drivers:
- For .exe files: Double-click and follow the installation wizard

- For .zip files: Extract them and use Device Manager to install
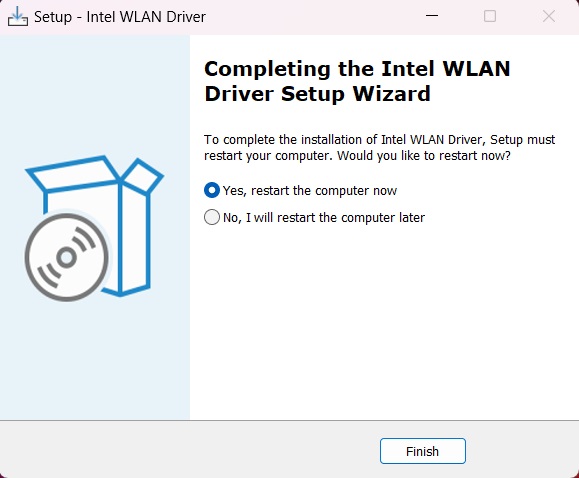
- Some installations may require a system restart

Best Practices for Driver Management
- Regular Maintenance: Check for driver updates monthly, keep Windows Update enabled, and document any hardware changes you make to your system.
- Troubleshooting: If a device stops working after an update, use the rollback feature in Device Manager, keep copies of working drivers before updating, and note down any error codes you encounter for easier troubleshooting.
- Safety Measures: Download drivers only from manufacturer websites or Windows Update, avoid updating drivers that are working properly, and always choose the correct version for your specific hardware model.
When to Seek Professional Help
Consider reaching out to professional support if:
- You encounter persistent blue screens after driver updates
- Hardware continues to malfunction after trying all update methods
- You’re unsure about specific hardware compatibility
- The system becomes unstable after driver installations
- Hardware is detected but shows up as “Unknown Device” in Device Manager and automatic detection methods fail
Remember that proper driver management is crucial for system stability and performance. By following these methods and best practices, you can maintain your Windows 11 PC in optimal condition while avoiding common driver-related issues.
Need help with a specific driver problem? Feel free to describe the issue in detail, and I’ll provide targeted guidance for your situation.